概述
以只有1个Servlet的简单情况为例,一般涉及到3个配置文件:web.xml,applicationContext.xml,xxx-servlet.xml。
web.xml
|
|
在这种情况下,系统会生成2个ApplicationContext,确切的说是2个WebApplicationContext.
ROOT ApplicationContext
在Tomcat启动时,通过注册的监听器ContextLoaderListener,Spring初始化WebApplicationContext并保存到ServletContext中,初始化使用的配置文件位置由contextConfigLocation参数确定。该Context为整个框架中的ROOT Context,其他的Context都会作为其子节点或子孙节点进行关联。
WebApplicationContext和ServletContext互相保存对方的引用:
|
|
|
|
xxx ApplicationContext
Tomcat生成xxx Servlet时,DispatcherServlet会使用xxx-servlet.xml(除非显示指定其他文件)初始化WebApplicationContext,将其父节点设为ROOT Context,并保存到ServletContext中。
在createWebApplicationContext()方法中,设置父节点:
|
|
在configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法中保存ServletContext:
|
|
在initWebApplicationContext()方法中将自己保存到ServletContext中:
|
|
ServletContext、ROOT Context和xxx Context三者引用之间的关系如下:
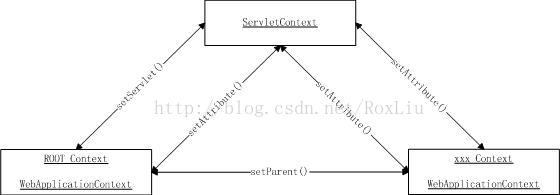
获取的方法:
- ServletContext:
无论是在ROOT还是xxx Context中,可以通过:
|
|
- ROOT Context:
该Context是” org.springframework.web.context. WebApplicationContext. ROOT”为Key保存在ServletContext中。可以使用Spring提供的工具类方法获取:
|
|
在xxx Context中可以通过getParent得到ROOT Context。
- xxx Context:
该Context是以” org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT.xxx”为KEY(xxx为web.xml中定义的Servlet名称),保存在ServletContext中。可以使用Spring提供的工具类方法获取:
|
|